满嘴都是糖果
Thread线程
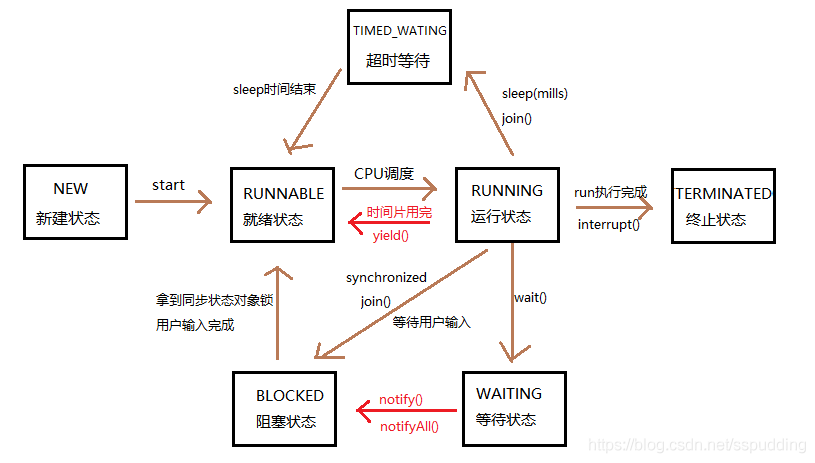
线程从创建到消亡包括以下几种状态:新建(new)、运行(running)、阻塞(blocked)、等待(waiting)、超时等待(timed waiting)、终止(terminated)。
- 新建(New) : 创建后尚未启动的线程处于这种状态。
- 运行(Runnable) : 包括操作系统线程状态中的Running和Ready, 也就是处于此状态的线程有可能正在执行, 也有可能正在等待着操作系统为它分配执行时间。
- 等待(Waiting) : 处于这种状态的线程不会被分配处理器执行时间, 它们要等待被其他线程显式唤醒。 以下方法会让线程陷入无限期的等待状态:
- 没有设置Timeout参数的Object::wait()方法;
- 没有设置Timeout参数的Thread::join()方法;
- LockSupport::park()方法。
- 超时等待(Timed Waiting) : 处于这种状态的线程也不会被分配处理器执行时间, 不过无须等待被其他线程显式唤醒, 在一定时间之后它们会由系统自动唤醒。 以下方法会让线程进入超时等待状态:
- Thread::sleep()方法;
- 设置了Timeout参数的Object::wait()方法;
- 设置了Timeout参数的Thread::join()方法;
- LockSupport::parkNanos()方法;
- LockSupport::parkUntil()方法。
- 阻塞(Blocked) : 线程被阻塞了, “阻塞状态”与“等待状态”的区别是“阻塞状态”在等待着获取到一个排它锁, 这个事件将在另外一个线程放弃这个锁的时候发生; 而“等待状态”则是在等待一段时间, 或者唤醒动作的发生。 在程序等待进入同步区域的时候, 线程将进入这种状态。
- 终止(Terminated) : 已终止线程的线程状态, 线程已经结束执行。
阻塞与等待
- 阻塞:当一个线程试图获取对象锁(非java.util.concurrent库中的锁,即synchronized),而该锁被其他线程持有,则该线程进入阻塞状态。它的特点是使用简单,由JVM调度器来决定唤醒自己,而不需要由另一个线程来显式唤醒自己,不响应中断。
- 等待:当一个线程等待另一个线程通知调度器一个条件时,该线程进入等待状态。它的特点是需要等待另一个线程显式地唤醒自己,实现灵活,语义更丰富,可响应中断。例如调用:Object.wait()、Thread.join()以及等待Lock或Condition。
start()
新启一个线程执行其run()方法,一个线程只能start一次。主要是通过调用native start0来实现。
public synchronized void start() {
//判断是否首次启动
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
//启动线程
start0();
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
private native void start0();
run()
run()方法是不需要用户来调用的,当通过start方法启动一个线程之后,当该线程获得了CPU执行时间,便进入run方法体去执行具体的任务。注意,继承Thread类必须重写run方法,在run方法中定义具体要执行的任务。
sleep()
sleep方法有两个重载版本
sleep(long millis) //参数为毫秒
sleep(long millis,int nanoseconds) //第一参数为毫秒,第二个参数为纳秒
sleep相当于让线程睡眠,交出CPU,让CPU去执行其他的任务。但是有一点要非常注意,sleep方法不会释放锁,也就是说如果当前线程持有对某个对象的锁,则即使调用sleep方法,其他线程也无法访问这个对象。
yield()
调用yield方法会让当前线程交出CPU权限,让CPU去执行其他的线程。它跟sleep方法类似,同样不会释放锁。但是yield不能控制具体的交出CPU的时间,另外,yield方法只能让拥有相同优先级的线程有获取CPU执行时间的机会。
注意,调用yield方法并不会让线程进入阻塞状态,而是让线程重回就绪状态,它只需要等待重新获取CPU执行时间,这一点是和sleep方法不一样的。
join()
join方法有三个重载版本:
join()
join(long millis) //参数为毫秒
join(long millis,int nanoseconds) //第一参数为毫秒,第二个参数为纳秒
join()实际是利用了Object的wait()方法,只不过它不用等待notify()/notifyAll(),且不受其影响。它结束的条件是:1)等待时间到;2)目标线程已经run完(通过isAlive()来判断)。
public final synchronized void join(long millis) throws InterruptedException {
long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
long now = 0;
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
//0则需要一直等到目标线程run完
if (millis == 0) {
while (isAlive()) {
wait(0);
}
} else {
//如果目标线程未run完且阻塞时间未到,那么调用线程会一直等待。
while (isAlive()) {
long delay = millis - now;
if (delay <= 0) {
break;
}
wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}
}
}
interrupt()
此操作会将线程的中断标志位置位,至于线程作何动作那要看线程了。
- 如果线程
sleep()、wait()、join()等处于阻塞状态,那么线程会定时检查中断状态位如果发现中断状态位为true,则会在这些阻塞方法调用处抛出InterruptedException异常,并且在抛出异常后立即将线程的中断状态位清除,即重新设置为false。抛出异常是为了线程从阻塞状态醒过来,并在结束线程前让程序员有足够的时间来处理中断请求。 - 如果线程正在运行、争用synchronized、lock()等,那么是不可中断的,他们会忽略。
可以通过以下三种方式来判断中断:
1、isInterrupted()
此方法只会读取线程的中断标志位,并不会重置。
2、interrupted()
此方法读取线程的中断标志位,并会重置。
3、throw InterruptException
抛出该异常的同时,会重置中断标志位。
suspend和resume由于可能会因为争锁的问题引发死锁,在JDK7以后不推荐使用了。